Enterprise Resource Planning – ERP
What Is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a system to database and integrate the important workflows of a business.

Who uses and business silos integrated?
- Sales,
- Finance,
- Purchasing,
- HR & Payroll,
- Manufacturing,
- Procurement & Sourcing,
- Supply Chain Management
Examples: 2021 Top Rated Manufacturing ERP

https://www.selecthub.com/manufacturing-software/
Providers
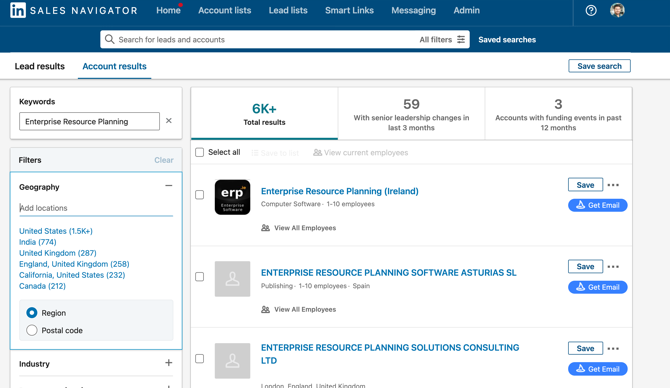
Over 6,000 Companies and almost 1 million related positions.
Implementation – 10 Best Practices For A Successful Implementation
- Define the problem you are trying to solve
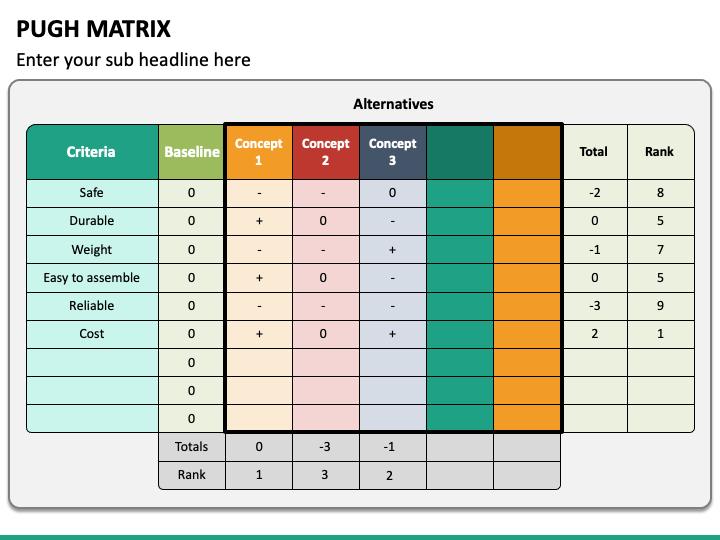
- Assign a Project Manager to spearhead start to finish. Use a Pugh Matrix for the decision-making process early on, set phases and define final deliverables/what completion looks like.
- Set up a team and mark calendar’s for preliminary and ongoing training
- Decide on a budget
- Check infrastructure and data worthiness. Map existing and new data flows.
- Built on a partnership with your vendor of choice, ensure a successful implementation is built into the contract.
- Avoid time consuming and high-cost customizations
- Leverage AI to find trends and keep you on the right path, it’s a marathon not a race.
- Run in a sandbox mode and test before setting live.
- Keep building, the system is only as good as what you put into it
Machine Execution System – MES
A key factor preventing manufacturers from utilizing data is the use of outdated manufacturing execution systems (MES). If companies want to capture the potential of Industry 4.0 or IIOT, they must evolve their MES (on-paper/software) to gain proactive insights from the data that they collect. The companies should understand that there is an alternate solution to this problem. It involves deploying central operational control towers to maximize productivity as they keep a tab of not a single work-center, but multiple machines or production lines. This helps the floor to increase efficiency, accuracy and productivity. They help in examining the data holistically.
The most modern approach in leveraging AI with your in-house MES will benefit across all products, processes, and equipment. It focuses on KPI (Key Performance Indicators) dashboards and data analytics solution. It uses the data-points across an array of data from the shop floor to provide AI-powered business insights. The data is collected from equipment, processes and quality departments – providing 80%+ data breakpoints in the shop floor. Then analysis of the data drives key insights that predict issues in advance. This can then scale into a true form of automation using AI and drive substantial benefits for any company.

Manufacturers are under pressure to transform – but MES constraints are real. They need to think differently. They need to think pragmatically. This module-based approach can help clients engage in either a greenfield (developed from scratch) or brownfield (working off an existing program) environment. It also helps in deploying solutions in a organic way and avoids a big bang disruptive approach.